Diamond Guide

Diamonds explained
Understanding diamonds is an essential part of choosing or designing a diamond ring, but how do you know which stone to choose? What even makes one diamond better than another? How do you know you’re making the right choice? Let our expertise guide you...
We'll help you make an informed choice that shines as brightly as your love, based on both fact and feeling.
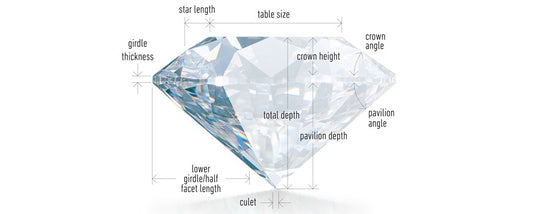
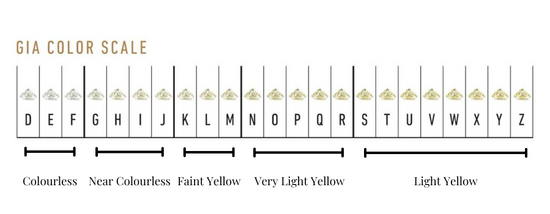
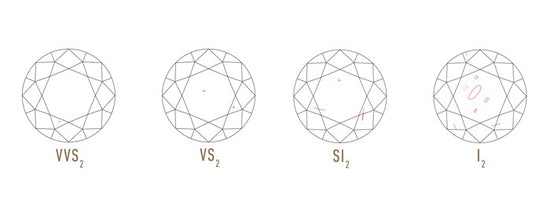
The 4Cs in Brief
Expert tip
Be sure to consider the diamond qualities along with other key aspects such as the ring setting, the wearer's lifestyle and fashion preferences, and most importantly - how the design makes them feel.
Beyond the 4Cs
Diamond shapes
Sometimes referred to as diamond cut, the shape of your diamond refers to the general silhouette of the stone rather than the quality of cut and arrangement of facets you read about in the 4Cs. In no particular order, here are some of the most popular diamond shapes to consider for ring.
-
1

The round cut is arguably the most recognisable diamond shape for an engagement ring. Virtually all round diamonds are brilliant-cut to enhance their fire and sparkle. A great all-rounder!
-
2

Oval diamonds have skyrocketed again in popularity recently, having first been seen as early as 1304. With similar fire and brilliance to round cut, they are elongated which increases the surface area and gets you a larger looking diamond for its weight.
-
3

Princess cut diamonds are another popular choice. Distinctively chic with its clean square shape, we'd call this diamond shape a modern classic. Many people opt for a prong setting to protect its four corners yet still let plenty of light through.
-
4

Emerald cut diamonds get their unique art-deco look from the step cuts which produce a stunning hall-of-mirrors effect. The long lines create brightness and shine and give the emerald cut an elegant appeal and luxurious glamour of a bygone era.
-
5

The pear or teardrop diamond is a statement look which is also gaining popularity. Partly thanks to their elongated shape, pear cuts look larger than a round diamond. And similar to the oval, they are actually larger on the surface, giving you more visible diamond for your money.
-
6

There's a whole host of other diamond shapes to consider, particularly if you're looking for a unique statement engagement ring. Marquise, Asscher, Cushion cut and even heart shaped diamonds are all contenders for something a little different.
Diamond buying guides
Still deciding on the shape and cut of diamond for your engagement ring? Find out more about these stunning and timeless styles in our diamond buying guides:
Round Brilliant Cut Diamond Buying Guide: What to Know
Ultimate Oval-Cut Diamond Buying Guide: Tips & Insights
Emerald Cut Diamond Buying Guide: Find Your Perfect Gem
Princess Cut Diamond Buying Guide: Sparkle & Style

Be inspired by
Solitaire engagement rings
A stunning solitaire makes the perfect engagement ring. Choose your favourite diamond shape and let the sparkling stone take centre stage.
Engagement rings